
Very soon after the
design of the Ki-43 Hayabusa had been started by Nakajima, the company
received instructions from the Imperial Japanese Army to initiate the
design of a new interceptor fighter. In this case however,
manoeuvrability was required to give precedence to overall speed and
rate of climb, and the company's design team selected the 1,250 hp (932
kw) Nakajima Ha-141 as the powerplant for this new project. Of similar
configuration to the Ki-43, the new Nakajima Ki-44 prototypes also
incorporated the manoeuvring flaps that had been introduced on that
aircraft, and carried an armament of two 7.7 mm (0.303 in) and two 12.7
mm (0.50 in) machine guns. First flown on August 1940, the Ki-44 was
involved in a series of comparative trials against Kawasaki's Ki-60
prototype, based on the use of the Daimler-Benz DB 601 engine, and an
imported Messerschmitt Bf 109E. The result of the evaluation and
extensive service trials, showed the Ki-44 to be good enough to enter
production, and it was ordered under the designation Army Type 2 Single
seat Fighter Model 1A Shoki (demon), company designation Ki-44-Ia,
which carried the same armament as the prototypes. A total of only 40
Ki-44-I aircraft was produced, including small numbers of the Ki-44-Ib
armed with four 12.7 mm (0.50 in) machine guns, and the similar
Ki-44-Ic with some minor refinements.

Nakajima Ki-44-IIb of the 23rd Sentai for home island defence in 1944
When introduced into
service the high landing speeds and limited manoeuvrability of the
Shoki made it unpopular with pilots, and very soon the Ki-44-II with a
more powerful Nakajima Ha-109 engine was put into production. Only
small numbers of the Ki-44-IIa similarly armed to the Ki-44-Ia, were
built, the variant being followed by the major production Ki-44-IIb
which apart from the different engine was identical to the Ki-44-Ic.
The Ki-44-IIc introduced much heavier armament, comprising of four 20
mm cannon or alternatively two 12.7 mm (0.50 in) machine guns and two
40 mm cannon, and these proved to be very effective when deployed
against Allied heavy bombers attacking Japan. However the increased
power had done nothing to eliminate the reasons for its unpopularity
with the pilots, and in fact, the higher wing loading of this version
meant that it had some violent reactions to high speed manoeuvres;
however, it later regained their respect because of its capability as
an interceptor.
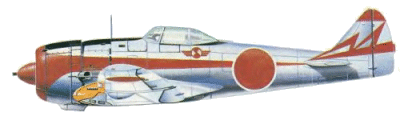
Nakajima Ki-44-IIb of the Shinten (air superiority) unit of the 47th
Sentai, Narimasu, Tokyo, summer 1944
Final production
version was the Ki-44-III with a 2,000 hp (1491 kw) Nakajima Ha-145
radial engine, an increase in wing area and enlarged vertical tail
surfaces, but comparatively few were built before production ended in
late 1944. They included the Ki-44-IIIa and the similar Ki-44-IIIb,
armed with four 20 mm cannon, and two 20 mm and two 37 mm cannon
respectively.
Nakajima had built a
total of 1,225 Ki-44's of all versions, including prototypes, and these
were allocated the Allied codename 'Tojo'. They were deployed primarily
in Japan, but were used also to protect vital targets, as in Sumatra
where they defended the oil fields at Palembang.
(Army Type 2 Single
Seat Fighter Model 1A Shoki "Demon" - Nakajima Ki-44-IIb)
Allied Codename:
Tojo
Type: Single
Seat Fighter Interceptor
Powerplant: One
1,520 hp (1133 kw) Nakajima Ha-109 (Type 2) 14-cylinder radial piston
engine.
Performance:
Maximum speed 376 mph (605 km/h) at 17,060 ft (5200 m); cruising speed
249 mph (400 km/h); service ceiling 36,745 ft (11200 m).
Range: 1,056
miles (1700 km) with internal fuel stores.
Weight: Empty
4,641 lbs (2105 kg) with a maximum take-off weight of 6,598 lbs (2993
kg).
Dimensions: Span
31 ft 0 in (9.45 m); length 28 ft 10 in (8.79 m); height 10 ft 8 in
(3.25 m); wing area 161.46 sq ft (15.00 sq m).
Armament: Two
12.7 mm (0.50 in) Type I (Ho-103) machine-guns in the upper decking
fuselage and two 12.7 mm (0.50 in) Type I (Ho-103) machine-guns mounted
in the wings.
Variants: Ki-44
(prototype SN 4401-4403), Ki-44-I(a) Army Type 2, Ki-44-Ib, Ki-44-Ic,
Ki-44-IIa (Nakajima Ha-109 Army Type 2 radial engine rated at 1,450
hp), Ki-44-IIb, Ki-44-IIc, Ki-44-IIIa, Ki-44-IIIb (Two 20 mm Ho-5
cannons and two 37 mm Ho-203 cannon).
Operators:
Japanese Army. |
