 Breakers
Breakers
radio and navigation receivers
left control yoke (P1)
 Magneto Switch
Magneto Switch
Switch
 Three-Control Power Quadrant
Three-Control Power QuadrantIncludes Carb Heat, Throttle,
and Mixture controls.
 Fuel Gauges and Load Amp Gauge, Oil Pressure Gauge, Oil Temperature Gauge, Fuel Pressure Gauge, and
Cylinder Temp Gauge.
Fuel Gauges and Load Amp Gauge, Oil Pressure Gauge, Oil Temperature Gauge, Fuel Pressure Gauge, and
Cylinder Temp Gauge.
 Registration Number
Registration Number Displays your official
registration, which air traffic controllers use to identify your
plane.
Clock
giving Greenwich
Mean Time or local time.
 Airspeed Indicator
Airspeed Indicator Displays how fast the plane is moving
relative to the air. Airspeed is measured in “knots,” or nautical miles travelled
per hour. An easy way to calculate your speed in miles per hour is to add 15 to
every hundred knots. In other words, if your aircraft was cruising at 100 knots,
you would be travelling at approximately 115 mph.
 Engine Tachometer
Engine TachometerLike a car’s tachometer, this indicates
the number of revolutions per minute (RPM) of the aircraft
engine.
 Turn
Coordinator
Turn
CoordinatorDisplays the rate and the direction of a horizontal turn.
The floating ball in the instrument helps the pilot prevent the airplane's tail
from skidding to the outside of a turn or slipping to the inside.
 Attitude Indicator
Attitude IndicatorAlso known as the “Artificial Horizon,”
this instrument displays the plane’s position relative to the ground and the
horizon. It is especially useful when conditions don’t allow clear vision
through the windshield.
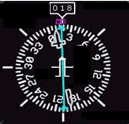
 Directional Indicator
Directional IndicatorIndicates the plane’s
heading
 Altimeter
Altimeter Displays your altitude. It reads like a clock,
with the big hand indicating hundreds of feet, and the little hand marking
thousands of feet.
 Vertical Speed Indicator
Vertical Speed IndicatorDisplays the plane’s rate of
climb or descent in feet per minute (fpm).
 VOR navigation indicators
VOR navigation indicatorsThe VOR navigation indicator gives
the pilot aircraft position information by means of three components. The track selector,
sometimes called the omnibearing selector or OBS, is used to rotate the azimuth ring, which
displays the selected VOR track. This ring may also show the reciprocal of the selected track.
The TO-FROM/OFF flag indicates whether the track will take the pilot to or from the station.
If the aircraft is out of station range and cannot receive a reliable, usable signal the TO-FROM/OFF
indicator displays OFF. Also, the OFF flag is displayed when the aircraft is directly over the station,
when abeam of the station in the area of ambiguity (i.e., directly on either side of the station) or when
beyond the reception range of the station selected.
 Audio Control Panel
Audio Control Panel Controls the messages that are sent
and received by the plane.
 Automatic Direction Finder (ADF)
Automatic Direction Finder (ADF)Some aircraft are equipped
with an ADF receiver. They receive radio signals in the medium frequency band of
190 Khz to 1750 Khz. The ADF receiver can “Home” on both AM radio stations and
Non-Directional Beacons. Commercial AM radio stations broadcast on 540 to 1620 Khz.
Non-Directional Beacons (NDBs) operate in the frequency band of 190 to 535 Khz.
 Transponder
Transponder Detects incoming radar signals and returns a
signal that allows a controller on the ground to identify and follow your plane
by radar. .
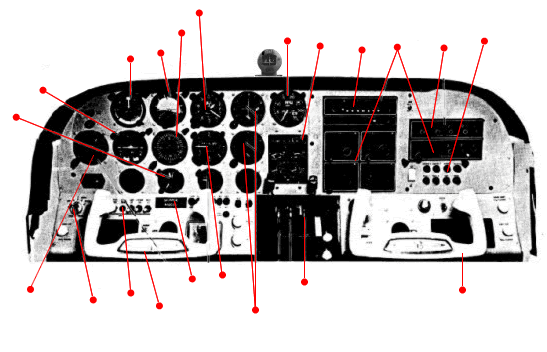
 Three-Control Power Quadrant
Three-Control Power Quadrant![]() Fuel Gauges and Load Amp Gauge, Oil Pressure Gauge, Oil Temperature Gauge, Fuel Pressure Gauge, and
Cylinder Temp Gauge.
Fuel Gauges and Load Amp Gauge, Oil Pressure Gauge, Oil Temperature Gauge, Fuel Pressure Gauge, and
Cylinder Temp Gauge. Airspeed Indicator
Airspeed Indicator  Engine Tachometer
Engine Tachometer Turn
Coordinator
Turn
Coordinator Attitude Indicator
Attitude Indicator Directional Indicator
Directional Indicator Altimeter
Altimeter  Vertical Speed Indicator
Vertical Speed Indicator VOR navigation indicators
VOR navigation indicators
